Diabetes is Australia’s fastest growing chronic condition. Diabetes is a serious complex condition which can affect the entire body. Diabetes requires daily self-care and if complications develop, diabetes can have a significant impact on the quality of life and can reduce life expectancy. While there is currently no cure for diabetes, you can live an enjoyable life by learning about the condition and effectively managing it.
Here are some key statistics about the different types of diabetes and the impact of the condition on the community.
- 1.8 million Australians are living with diabetes – this includes 1.3 million people who have been diagnosed and an estimated 500,000 cases of undiagnosed type 2 diabetes.
- Every five minutes someone is diagnosed with diabetes, which adds up to almost 300 people every day.
- One in four adults over the age of 25 is living with either diabetes or pre-diabetes.
- Diabetes is the seventh most common cause of death by disease in Australia.
- Diabetes costs the Australian economy $14 billion every year.
All types of diabetes are increasing in prevalence:
- Type 1 diabetes accounts for 10% of all diabetes and is increasing
- Type 2 diabetes accounts for 85% of all diabetes and is increasing
- Gestational diabetes in pregnancy is increasing
Type 1 Diabetes:
- 119,000 Australians are currently living with type 1 diabetes
- Represents 10 to 15 per cent of all cases of diabetes and is increasing each year
- Occurs when the cells of the pancreas are destroyed by the body’s immune system, meaning that the body is unable to produce any insulin
- Requires treatment with ongoing insulin therapy
- Is not caused by lifestyle factors and has no known cause or cure
- Is often diagnosed in childhood, although it can occur at any age.
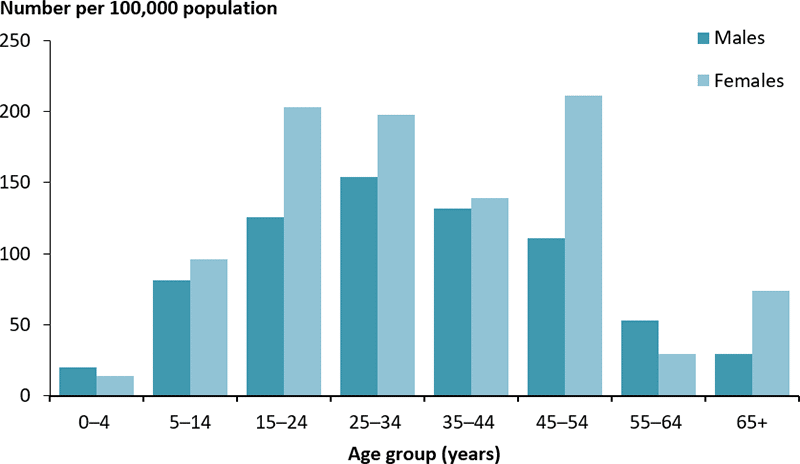
Type 2 Diabetes:
- 1.3 million Australians are currently living with type 2 diabetes.
- Represents 85 to 90 per cent of all cases of diabetes and is increasing each year.
- Occurs when the pancreas is not producing enough insulin, or when the insulin that is produced is not working effectively.
- Risk factors include age, family history, ethnicity and lifestyle factors such as an unhealthy diet and lack of physical activity.
- 58 per cent of all cases of type 2 diabetes can be delayed or prevented with changes to diet and lifestyle.

Gestational Diabetes:
- Affects one in seven pregnancies.
- Is the fastest growing type of diabetes in Australia.
- Occurs during pregnancy and usually goes away after the baby is born.
- Women who have had gestational diabetes are at greater risk of developing type 2 diabetes later in life.
- Risk factors include age, ethnicity and being above a healthy weight range when pregnant.
- Gestational diabetes may also occur in women with no known risk factors and should be tested for at 24–28 weeks of pregnancy.
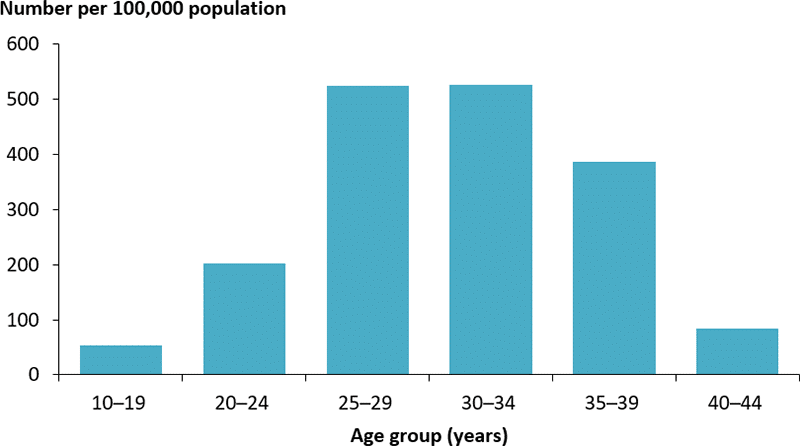
Myths About Diabetes
There are many myths about diabetes which can make separating fact from fiction difficult. To cut through the confusion, we’ve broken down some of the common misconceptions:
Myth – Diabetes is not serious
Fact – There is no such thing as “mild” diabetes. All types of diabetes are serious and can lead to complications if not well managed. Diabetes can affect quality of life and can reduce life expectancy.
Myth – All types of diabetes are the same
Fact – There are a number of types of diabetes. The most common are type 1, type 2 and gestational diabetes Other forms of diabetes are less common. Each type of diabetes has different causes and may be managed in different ways but once someone has any type of diabetes except gestational diabetes, it needs to be managed every day. Gestational diabetes goes away after pregnancy, however, it does significantly increase someone’s risk of developing type 2 diabetes later in life. All types of diabetes are complex and serious.
Myth – Diabetes can be prevented
Fact – Not all types of diabetes can be prevented. Type 1 is an autoimmune condition, it cannot be prevented and there is no cure. The cause of type 1 diabetes is still unknown.
Strong international evidence shows diabetes prevention programs can help prevent type 2 diabetes in up to 58 per cent of cases. There is no single cause of type 2 diabetes, but there are well-established risk factors. Your risk of developing diabetes is also affected by things you cannot change such as family history and ethnicity.

Myth – You have to be overweight or obese to develop diabetes
Fact – Being overweight or obese is a risk factor for type 2 diabetes but it is not a direct cause. Some people who are overweight may not develop type 2 diabetes while some people who are of a healthy weight will develop type 2 diabetes.
Type 1 diabetes is not preventable and not associated with weight, physical inactivity or any other lifestyle factors.
Myth – You only get type 1 diabetes when you’re young
Fact – The onset of type 1 diabetes occurs most frequently in people under 30 years, however, new research suggests almost half of all people who develop the condition are diagnosed over the age of 30.
Myth – You only get type 2 diabetes when you’re old
Fact – Type 2 diabetes usually develops in adults over the age of 45 years but is increasingly occurring in younger age groups including children, adolescents and young adults.
Myth – People with diabetes can’t eat dessert
Fact – Because diabetes affects blood glucose levels, many people think they need to avoid sugars and foods containing sugar. However, if eaten as part of a healthy meal plan, or combined with exercise, sweets and desserts can be eaten by people with diabetes. The key is to eat everything in moderation.
The Australian Dietary Guidelines are recommended for people with all types of diabetes as well as the rest of the population. For your individual dietary needs, we recommend seeing an Accredited Practicing Dietitian and talking to your diabetes healthcare team about the right approach to help you live well with your diabetes.
Myth – People with type 1 diabetes can’t participate in sports or exercise
Fact – Many Australian sports champions have type 1 diabetes. Read our profile on AFL player Jack Fitzpatrick who plays for the Melbourne Football Club.
Myth – No one in my family has diabetes so I don’t have to worry
Fact – Family history is only one of the risk factors for type 2 diabetes.
Myth – People with diabetes are unsafe drivers
Fact – The vast majority of drivers who use insulin can drive safely. Learn more here.
Myth – Only people with type 1 diabetes need insulin
Fact – Type 2 diabetes is a progressive condition. 50 percent of people with type 2 diabetes will need insulin after 6-10 years of being diagnosed with diabetes because the pancreas produces less insulin over time. Taking medication when required can result in fewer complications in the long-term and is part of managing type 2 diabetes.
People with type 1 diabetes depend on insulin replacements every day of their lives. They must test their blood glucose levels several times throughout the day.
Sources:
- https://diabetesnsw.com.au/about-diabetes/what-is-diabetes/facts-and-figures/
- https://www.diabetesaustralia.com.au/myths-facts
- https://www.aihw.gov.au/reports/diabetes/diabetes-indicators-strategy-2016-2020/contents/goal-5






























